Troponin I
The biomarker of choice to aid the diagnosis of myocardial infarction
-
 Fast Results
Fast Results
-
 Risk stratification of patients with ACS
Risk stratification of patients with ACS
-
 No interference from Hemolysis and Biotin*
No interference from Hemolysis and Biotin*
Troponin tests at the emergency department
When a patient arrives at the emergency department (ED) with chest pain and no or unclear changes on the electrocardiogram (ECG), the ED physician typically orders serial troponin tests [1].
This is to establish if the symptoms are caused by an acute myocardial infarction (AMI) - a heart attack - and to determine the next steps which could either be ruling in a patient for an intervention—or ruling the patient out [1].
*No interference from Biotin up to 2.6 mg/L (2,600 ng/mL).
Immunoassay products and solutions

Troponins are specific markers of cardiac muscle injury
Troponins are proteins of the muscular thin filaments and part of a complex in striated muscle [2].
Cardiac troponins are components of the contractile apparatus of myocardial cells and are expressed almost exclusively in the heart and are the preferred biomarker for the evaluation of myocardial injury. Myocardial injury is defined as being present when blood levels of cTn are increased above the 99th percentile upper reference limit (URL). When the injury is associated with a rising and/or falling pattern of cTn values it indicates myocardial ischaemia and is designated as an acute myocardial infarction [3].

Troponins - an aid in diagnosing myocardial infarction
For patients with myocardial infarction, the timing of biomarker release into the blood stream is dependent on the patient's blood flow. Accodringly, measured biomarker concentrations are dependent on how soon after the onset of symptoms, samples are obtained [3].
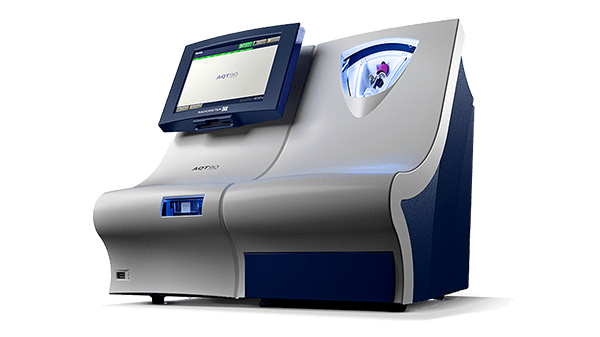
Troponin tests on the AQT90 FLEX analyser
The AQT90 FLEX TnI test is indicated for use as an aid in diagnosing myocardial infarction and in the stratification of patients with acute coronary syndromes.
The AQT90 FLEX analyser delivers quantitative results on the TnI in less than 19 minutes, accelerating myocardial infarction diagnosis in the ED to support rapid clinical decision making.
Its closed tube system makes troponin testing easy: the operator simply inserts the sample tube into the tube holder in the sample port and the analyser performs all assay steps automatically. There is no need for sample preparation.
All necessary reagents are included in the test cartridges, which remain stable onboard the analyser for 17 days ensuring maximum availability and uptime.
Key benefits of Troponin I on the AQT90 FLEX analyser
- No blood exposure: closed system
- No sample or assay preparation
- No presence of hook effect, carry-over or known interferences at clinically relevant concentrations
- Interference from heterophilic antibodies are minimised by adding a blocker substance
- Specimen types: venous whole blood and plasma
- Sample tubes: Fits most 13 × 75 mm standard tubes
References
2. Welsh P, Preiss D, Sattar N. Utility of High-Sensitivity Troponin T and I: Are They the Same? Expert analysis in American College of Cardiology (acc.org) Assessed Nov 2021.
3. Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al., Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction J Am Coll Cardiol Oct 2018; 72(18):2231-2264
Cookies are used on this website
Use of cookiesPlease enter a valid email
We will be sending an e-mail invitation to you shortly to sign in using Microsoft Azure AD.
It seems that your e-mail is not registered with us
Please click "Get started" in the e-mail to complete the registration process
Radiometer is using Microsoft AZURE Active Directory to authenticate users
Radiometer uses Azure AD to provide our customers and partners secure access to documents, resources, and other services on our customer portal.
If your organization is already using Azure AD you can use the same credentials to access Radiometer's customer portal.
Key benefits
- Allow the use of existing Active Directory credentials
- Single-sign on experience
- Use same credentials to access future services
Request access
You will receive an invitation to access our services via e-mail when your request has been approved.
When you accept the invitation, and your organization is already using AZURE AD, you can use the same credentials to access Radiometer's customer portal. Otherwise, a one-time password will be sent via e-mail to sign in.