
Causes of needlestick injury
The unavailability of sampling safety devices for operators or the lack of a dedicated procedure for operator safety can lead to needlestick injuries. [1-3]
Risks of needlestick injury
Needlestick injury may lead to safety concerns or infection by blood-borne pathogens. [1]
Healthcare professionals are at risk of being exposed to blood-borne pathogens through coming into contact with blood. Such contact can be a result of inoculation of blood by a needle. [4]
Minimize needlestick injury with a needleshield device
A needleshield works in accordance with the EU directive 2010/32/EU for the prevention of sharp injuries within hospitals. [5]
Sharps need to be disposed safely and immediately into appropriate, puncture-proof bins to protect you from blood-borne pathogens.
To protect healthcare professionals from accidental needlestick injuries, the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines recommends the use of engineered sharps injury protection. [6]
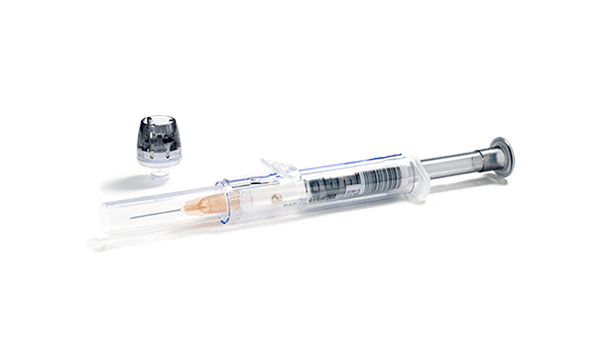
The safePICO arterial blood gas syringe with needleshield device
The safePICO syringe contains a needleshield device that is securely locked. After activating the needleshield, you dispose the needle securely and minimize the risk of needlestick injury.

References
2. Fukuda H, Yamanaka N. Reducing needlestick injuries through safety-engineered devices: results of a Japanese multi-center study. J Hosp Infec. 2016 Feb; 92(2); 147-153.
3.Tosini et al. Needlestick injury rates according to different types of safety-engineered devices: results of a French multicenter study. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2010 Apr; 31(4) 402-407.
4. European Agency for Safety and Health at Work. Risk assessment and needlestick injuries. https://osha.europa.eu/en/tools-and-publications/publications/e-facts/efact40. Accessed October 2022.
5. Official Journal of the European Union. Council Directive 2010/32/EU of 10 May 2010, Implementing the Framework Agreement on prevention from sharp injuries in the hospital and healthcare sector concluded by HOSPEEM and EPSU. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32010L0032&from=EN Accessed October 2022.
6. CLSI. Procedures for the Collection of Arterial Blood Specimens; Approved Standard—Fourth Edition. CLSI document GP43-A4 [ISBN 1-56238-545-3). Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 950 West Valley Road, Suite 2500, Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087 USA, 2004.
Cookies are used on this website
Use of cookiesPlease enter a valid email
We will be sending an e-mail invitation to you shortly to sign in using Microsoft Azure AD.
It seems that your e-mail is not registered with us
Please click "Get started" in the e-mail to complete the registration process
Radiometer is using Microsoft AZURE Active Directory to authenticate users
Radiometer uses Azure AD to provide our customers and partners secure access to documents, resources, and other services on our customer portal.
If your organization is already using Azure AD you can use the same credentials to access Radiometer's customer portal.
Key benefits
- Allow the use of existing Active Directory credentials
- Single-sign on experience
- Use same credentials to access future services
Request access
You will receive an invitation to access our services via e-mail when your request has been approved.
When you accept the invitation, and your organization is already using AZURE AD, you can use the same credentials to access Radiometer's customer portal. Otherwise, a one-time password will be sent via e-mail to sign in.

